Wave Picking
In the last post we saw the various types of picking methodologies available for a warehouse manager to choose from, such as Batch Picking, Zone Picking, Consignment / Order Based Picking and Wave Picking. Amongst these, Wave Picking by itself is a subject area in itself. And hence this post.
What is Wave Picking?
Wave Picking is a scheduled order picking process, executed in short duration, multiple times in a day, in which multiple customer orders having disparate SKU’s are picked up by multiple pickers at the same time. A typical Wave would be scheduled to last, depending on the size of the warehouse and type of SKU, between 30 and 60 min’s.
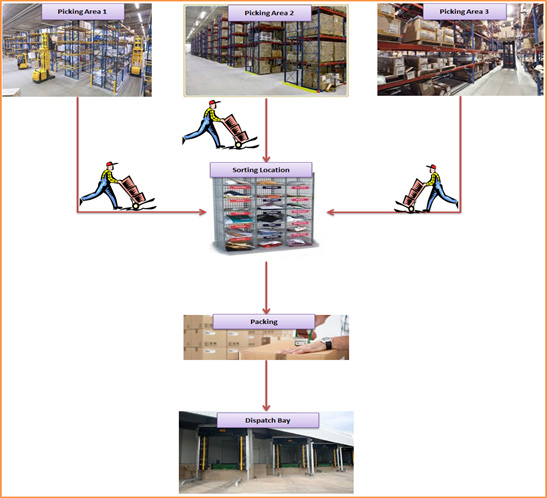
A sample wave picking flow is described below:
Wave Picking Image:
How does Wave Picking Work?
Wave Picking as mentioned earlier is a scheduled short duration picking operation. Let us consider a scenario where a Wave is scheduled every 1 hour.
Apart from the wave schedule the following parameters need to be defined:
- Shifts / day : 1
- Operation Time : 09:00 to 17:00
- Break Time : 13:00 to 14:00
- Wave First Run Time : 08:00 a.m.
Considering the above parameters the first Wave will get generated for 08:00 a.m. for 09:00 a.m. picking, the second wave will get generated at 09:00 a.m. for 10 a.m. picking, so on and so forth. In each wave, all orders are consolidated and based on preconfigured parameters, multiple picking instructions are generated. The generated picking instruction for a picker will include similar types of SKU’s for different orders form the same location. This ensures that the picking operator does not have to unnecessarily travel across the warehouse to pick up SKU’s.
All picking operators drop the SKU’s to a centralised Sorting Location. The sorting operator then proceeds to sort the SKU’s according to their order numbers. Once the sorting operations are completed, the SKU’s are sent for packaging and after packing to the dispatch bay, from where the material is shipped to the customer.
How to Implement / Configure Wave Picking?
To implement wave picking a few fundamental questions have to be answered
- How to select orders
- How to assign picks
- How to give sorting instructions
- How to group dispatches
Let us see how this can be achieved:
How to Select Orders?
Order selection is the first and an extremely important step in Wave Picking process. While selecting which orders to process in the wave, some of the criteria that should be considered are:
- Order Type
- Order Age
- Transportation Lead Time
- Distance from Warehouse to Customer Location
- Truck Dispatch Time / Courier Pickup Time
The above criterion ensures that no order is left unfulfilled. Apart from the above mentioned criterion, the other important criterion is to configure the picking cut off time. Picking cut off time specifies, the cut off time for SKU’s to be shipped at a particular point of time. For example, consider that a truck / courier is scheduled to leave for Bangalore at 14:00. Picking cut off time will specify the maximum time till orders can be picked for the 14:00 dispatch. The points to be considered for specifying the cut off time are:
- Picking Lead Time
- Sorting Lead Time
- Packing Lead Time and
- Loading Lead Time
This approach also ensures that in case truck capacity is not fulfilled the maximum SKU’s for Bangalore route would be picked up as the cut off time draws closer.
How to Assign Picks?
Once the orders are selected, the orders need to be assigned to picking operators. This is an important process because if picks are not assigned properly it may result in delayed or incorrect picks.
The most important points to be considered while assigning picks are:
- Picking Capacity per Person
- Traversal time from
b.1) Sorting Area to Aisle
b.2) Average Picking Time for a SKU at that location
b.3) Traversal time from one end of the aisle to the other end of the aisle
b.4) Aisle to Aisle traversal time - Total picking time available
- MHE dependent location
- Number of Pickers available
There are three options to arrive at number of pickers available, they are:
- Integrate with Attendance Management System to identify number of pickers available
- Assume infinite set of pickers
- Define number of pickers available and assume all the pickers are present
The best option would be to integrate with Attendance Management System of the client. This will ensure that the picks assigned are realistic and will not overburden the picker. In the other two options as the actual number of pickers are not known, efficiency of the wave can get compromised and impact subsequent waves.
When the picking operator picks a SKU from a location, a picking label should be attached to the SKU. The picking label will have all the relevant details of the order as well as information required for sorting and packing.
How to Give Sorting Instructions?
As wave picking involves picking SKU’s for different orders at the same time, items have to be sorted according to the order numbers. Sorting instructions can be given in two ways:
- Sort to Light
- Instruction based sorting
Sort to Light:
In this methodology, when the sorting operator scans the picking label barcode, a sorting location lights up, giving the operator a visual instruction.
The disadvantage in this method is that only one sorting operator can carry out the sorting operation at any given point of time.
Instruction Based Sorting:
In this methodology, when the sorting operator scans the picking label, the sorting location is displayed on the HHT device used by the operator.
In instruction based sorting method, we can assign multiple sorting operators to a location, thereby increasing the sorting efficiency.
How to group dispatches
After sorting operation is completed, the SKU’s will be packed and placed in the dispatch bay. To ensure that all the picked material is dispatched on time while taking care of truck efficiency is very important. If truck efficiency is not maintained it will directly add to the operations cost of the company.
Grouping of dispatches and truck loading should ideally be carried out based on the route travelled by the truck and the number of delivery hub’s located in that particular route. That is to say, if the origin point of the truck is Mumbai and its destination is Bangalore, then the truck should ideally contain material for all the hub’s falling in that particular route. This is similar to the milk run concept. This approach ensures that the truck always meets its efficiency threshold.
Conclusion:
Wave picking is an interesting concept but is best suited for situations where huge numbers of disparate SKU’s are being ordered every hour, similar to the ecommerce industry. Wave picking can also significantly increase operational complexity and add to the overhead of the company if not implemented correctly. Some of the common points are:
- Identifying / Planning Required Manpower
- Dedicated Sorting Locations
- Having Dedicated Dispatch Bay’s for a Route
Wave Picking Implementation in PALMS©
Apart from the traditional picking methodologies, PALMS© provides a powerful implementation of wave picking as an add-on module. The wave picking module takes into account all the points explained above. In addition to the above points PALMS© provides the following features
- Promotional Wave Configuration: This option can be used during promotions or campaigns, where you can configure the parameters according to the promotion or campaign being run. This can be configured for an hour / day / week / month.
- Pin (ZIP) Code based Hub and Route grouping and configuration
- Integration with ASRS systems
- Web based and HHT based operations
